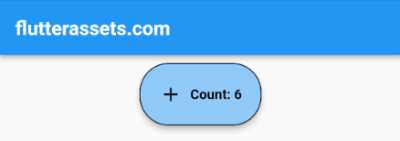
Custom button with a counter inside in Flutter
To create a counter inside an ElevatedButton in Flutter, you can use a StatefulWidget to manage the counter value and update it when the button is pressed. For a more customized button, you can use the ElevatedButton.icon widget and add the ADD icon inside the button. You can also use the style property of ElevatedButton to give the button a circular shape with larger borders. Finally, you can add a border to the button using the BorderSide class.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to create a counter inside an ElevatedButton with these customizations:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class CounterButton extends StatefulWidget {
final ValueSetter<int> onCountChanged;
CounterButton({required this.onCountChanged});
@override
_CounterButtonState createState() => _CounterButtonState();
}
class _CounterButtonState extends State<CounterButton> {
int _count = 0;
void _incrementCount() {
setState(() {
_count++;
widget.onCountChanged(_count); // notify parent widget of count change
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ElevatedButton.icon(
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
elevation: 5,
foregroundColor: Colors.black,
backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade200,
shape: const RoundedRectangleBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(30))
),
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
side: BorderSide(color: Colors.black, width: 1),
),
onPressed: _incrementCount,
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
label: Text('Count: $_count'),
// child: Text('Count: $_count'),
);
}
}In this code, we’ve created a CounterButton widget that takes a ValueSetter<int> callback as a parameter. This callback is called every time the counter value is changed and can be used to print or store the counter value. Inside the widget, we’ve used a StatefulWidget to manage the counter value and update it when the button is pressed. We’ve also used the ElevatedButton.icon widget to create the button with the ADD icon inside. Finally, we’ve used the style property of ElevatedButton to give the button a circular shape with larger borders and added a border to the button using the BorderSide class.
To use the CounterButton widget in another widget, we can simply add it to the widget tree and provide a callback to handle the count change event:
import 'counterButton.dart'; // This is the name of the new counter button dart filebody: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: CounterButton(
onCountChanged: (count) {
print('Count changed: $count');
},
),
),In this example, we used the CounterButton inside a Container. We provide a callback that prints the new count value to the console whenever the count changes. This is just one example of how the count value could be used – the actual behaviour will depend on the requirements of the app or widget.
How to make a counter with two buttons in Flutter
To create a counter in Flutter with a row widget, two iconButtons, and a text widget, you can use the following steps:
In the build method of the state class, create a Row widget that contains two IconButtons and a Text widget. The IconButtons will be used to increment and decrement the counter value, while the Text widget will display the current value of the counter.
Assign an onPressed callback to each IconButton that will increment or decrement the counter value when the button is pressed. You can use the setState method to update the state of the widget and redraw it with the new value.
Here’s an example code that demonstrates how to create a counter in Flutter with a row widget, two iconButtons, and a text widget:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage>{
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter--;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('flutterassets.com'),
),
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 24.0),
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.remove),
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
),
],
)
),
);
}
}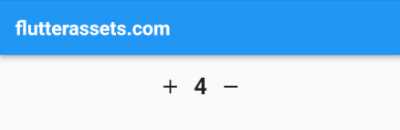
The code contains the counter value and manages its state. In the state class, we define two methods _incrementCounter and _decrementCounter that increment and decrement the counter value respectively.
In the build method, we create a Row widget that contains two IconButtons and a Text widget. The Text widget displays the current value of the counter, which is stored in the _counter variable. We assign an onPressed callback to each IconButton that calls the corresponding method to update the counter value and redraw the widget with the new value.
Customize the counter in the Raw widget
To customize the above code response, we can wrap the Row widget with a Container and set the width of the container to the width of the device screen and the height to 80. We can also add a border radius of 30 to the container to give it a rounded look.
To evenly distribute the IconButtons and Text widget within the container, we can change the mainAxisAlignment of the Row widget to spaceBetween.
Here’s an updated version of the code with these changes:
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Container(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width,
height: 80,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(30),
color: Colors.grey[200],
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 24.0),
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.remove),
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
),
],
),
)
),
Customize the counter buttons
to customize the above code, we can add some variables to allow for more flexible styling. For example, we can add variables to control the size and colour of the IconButtons. In this case, we can set iconSize to 50 and color to Colors.red.
Here is the modified version of the code:
int _counter = 0;
double _iconSize = 50;
Color _iconColor = Colors.red;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter--;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('flutterassets.com'),
),
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Container(
height: 80,
width: double.infinity,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(30),
color: Colors.grey[200],
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
iconSize: _iconSize,
color: _iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.remove),
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
),
VerticalDivider(),
Spacer(),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30),
),
Spacer(),
VerticalDivider(),
IconButton(
iconSize: _iconSize,
color: _iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
),
],
),
)
),
);
}
In this updated code, we added two new variables: iconSize and iconColor. We can use these to customize the size and colour of the IconButtons.
We also added a VerticalDivider after the first IconButton and a Spacer to the right of the VerticalDivider. Similarly, we added a Spacer to the left of the second IconButton and a VerticalDivider to the right of the Text widget. These VerticalDividers help to create a visual separation between the various components within the Row widget.
I also switched the buttons :).
Customize the counter value display
Here we modified the above code a bit more:
int _counter = 0;
double _iconSize = 50;
Color _iconColor = Colors.red;
String _counterLabel = "Counter";
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter--;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('flutterassets.com'),
),
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Container(
height: 80,
width: double.infinity,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(30),
color: Colors.grey[200],
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
iconSize: _iconSize,
color: _iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.remove),
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
),
VerticalDivider(),
Expanded(
child: Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 4),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(5),
color: Colors.grey[100],
),
child: Row(
children: [
Spacer(),
Column(
children: [
Text(_counterLabel, style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20),),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 30),
),
],
),
Spacer(),
],
),
),
),
VerticalDivider(),
IconButton(
iconSize: _iconSize,
color: _iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
),
],
),
)
),
);
}
In the above code, we wrapped our text widget with a few other widgets like Expanded and a Row. s section is responsible for displaying the counter value. The Expanded widget is used to expand the middle container to fill the remaining space between the first and last IconButton widgets.
Inside the Expanded widget, there is a Container widget with a grey background and rounded borders. This container has a Row widget as a child that contains a Spacer, a Column widget, and another Spacer.
The first Spacer widget is used to push the Column widget to the right, so it appears in the centre of the container.
The Column widget contains two Text widgets, the first displays the counter label which is stored in the _counterLabel variable, and the second displays the current counter value which is stored in the _counter variable.
The second Spacer widget is used to push the Column widget to the left, so it appears in the centre of the container.
Horizontal Counter Widget with two buttons in Flutter
This code is an improved version of the above counter that is designed as a custom widget called CustomCounter and the new Dart file name is “custom_counter.dart”.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class CustomCounter extends StatefulWidget {
final String counterLabel;
final bool labelVisible;
final double iconSize;
final Color iconColor;
final double counterHeight;
final double counterWidth;
final double counterLabelFontSize;
final double counterTextFontSize;
final Color counterTextColor;
final double borderRadius;
final Color borderColor;
final Color counterColor;
final Color displayColor;
final ValueSetter<int> callback;
const CustomCounter({
this.counterLabel = 'Counter',
this.labelVisible = true,
this.iconSize = 30,
this.iconColor = Colors.red,
this.counterHeight = 80,
this.counterWidth = double.infinity,
this.counterLabelFontSize = 20,
this.counterTextFontSize = 30,
this.counterTextColor = Colors.black,
this.borderRadius = 30,
this.borderColor = Colors.red,
this.counterColor = const Color(0xFFEEEEEE),
this.displayColor = const Color(0xFFF5F5F5),
required this.callback,
});
@override
_CustomCounterState createState() {
return _CustomCounterState();
}
}
class _CustomCounterState extends State<CustomCounter> {
int counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter++;
widget.callback(this.counter);
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter--;
widget.callback(this.counter);
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
height: widget.counterHeight,
width: widget.counterWidth,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(widget.borderRadius),
border: Border.all(color: widget.borderColor, width: 1.0),
color: widget.counterColor,
),
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
iconSize: widget.iconSize,
color: widget.iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.remove),
onPressed: _decrementCounter,
),
VerticalDivider(),
Expanded(
child: Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 2),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(5),
color: widget.displayColor,
),
child: Row(
children: [
Spacer(),
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Visibility(
visible: widget.labelVisible,
child: Text(
widget.counterLabel,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: widget.counterLabelFontSize,
color: widget.counterTextColor
),
),
),
Text(
'$counter',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: widget.counterTextFontSize,
color: widget.counterTextColor
),
),
],
),
Spacer(),
],
),
),
),
VerticalDivider(),
IconButton(
iconSize: widget.iconSize,
color: widget.iconColor,
icon: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
),
],
),
);
}
}This widget has various configuration options such as counterLabel, labelVisible, iconSize, iconColor, counterHeight, counterWidth, counterLabelFontSize, counterTextFontSize, counterTextColor, borderRadius, borderColor, counterColor, displayColor, and a callback function callback.
The process of converting the first code to the second code involves creating a new widget class CustomCounter that extends StatefulWidget. The counter value is moved into the widget state _CustomCounterState and is updated using the setState() method within the _incrementCounter and _decrementCounter methods. The configuration options in the first code are converted into properties of the CustomCounter widget. The IconButton and Row widgets in the first code are replaced with the corresponding widgets in the CustomCounter widget.
The end result is a more flexible and configurable counter widget that can be easily reused in other applications.
Here are the parameters of the CustomCounter widget:
counterLabel: AStringthat sets the label of the counter widget. Default value is'Counter'.labelVisible: Aboolthat determines if the label is visible or not. Default value istrue.iconSize: Adoublethat sets the size of the add and remove icons. Default value is30.iconColor: AColorthat sets the colour of the add and remove icons. Default value isColors.red.counterHeight: Adoublethat sets the height of the counter widget. Default value is80.counterWidth: Adoublethat sets the width of the counter widget. Default value isdouble.infinity.counterLabelFontSize: Adoublethat sets the font size of the counter label. Default value is20.counterTextFontSize: Adoublethat sets the font size of the counter value. Default value is30.counterTextColor: AColorthat sets the colour of the counter label and value text. Default value isColors.black.borderRadius: Adoublethat sets the border radius of the counter widget. Default value is30.borderColor: AColorthat sets the colour of the border of the counter widget. Default value isColors.red.counterColor: AColorthat sets the background colour of the counter widget. Default value isColor(0xFFEEEEEE).displayColor: AColorthat sets the background colour of the counter value display area. Default value isColor(0xFFF5F5F5).callback: a function that takes an integer parameter and returns nothing. This callback function is called every time the counter value is incremented or decremented.
All of these parameters can be set when you use the CustomCounter widget in your app. This allows you to customize the appearance and behaviour of the counter widget to fit your needs. Below is a code example of how to use the CustomCounter widget in the project.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'custom_counter.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage>{
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('flutterassets.com'),
),
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child:
Column(
children: [
CustomCounter(
counterHeight: 50,
counterWidth: double.infinity,
// counterLabel: 'Label',
labelVisible: false,
// counterLabelFontSize: 10,
counterTextFontSize: 24,
counterTextColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
iconSize: 20,
iconColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
displayColor: Colors.green.shade100,
counterColor: Colors.green.shade200,
borderRadius: 10,
borderColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
callback: (counter) {
print('$counter');
},
),
SizedBox(height: 10,),
CustomCounter(
callback: (counter) {
print('$counter');
},
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
To use the CustomCounter widget, you need to import the custom_counter.dart file which contains the definition of the CustomCounter widget. Then you can create an instance of the CustomCounter widget with the desired parameters and add it to the widget tree.
In the above code, the CustomCounter widget is used twice inside a Column widget. The first instance of CustomCounter widget has several parameters set, such as counterHeight, counterWidth, labelVisible, counterTextColor, displayColor, etc. These parameters customize the appearance and behaviour of the CustomCounter widget. The second instance of CustomCounter widget has only the callback parameter set, which is a function that gets called whenever the counter value changes.
To summarize, to use the CustomCounter widget, you need to:
- Import the
custom_counter.dartfile - Create an instance of the
CustomCounterwidget with the desired parameters - Add the
CustomCounterwidget to the widget tree
In this code, the CustomCounter widget is used inside a Column widget, but you can use it inside any other widget that accepts child widgets, such as Container, Row, ListView, etc.
Vertical Counter Widget with two buttons in Flutter
Here is a converted code from the above example. The new code creates a custom vertical counter. This new Dart file in called “custom_vertical_counter.dart”.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class CustomVerticalCounter extends StatefulWidget {
final String counterLabel;
final bool labelVisible;
final double iconSize;
final Color iconColor;
final double counterHeight;
final double counterWidth;
final double counterLabelFontSize;
final double counterTextFontSize;
final Color counterTextColor;
final double borderRadius;
final Color borderColor;
final Color counterColor;
final Color displayColor;
final ValueSetter<int> callback;
const CustomVerticalCounter({
this.counterLabel = 'Counter',
this.labelVisible = true,
this.iconSize = 30,
this.iconColor = Colors.red,
this.counterHeight = 250,
this.counterWidth = 70,
this.counterLabelFontSize = 14,
this.counterTextFontSize = 30,
this.counterTextColor = Colors.black,
this.borderRadius = 30,
this.borderColor = Colors.red,
this.counterColor = const Color(0xFFEEEEEE),
this.displayColor = const Color(0xFFF5F5F5),
required this.callback,
});
@override
_CustomVerticalCounterState createState() {
return _CustomVerticalCounterState();
}
}
class _CustomVerticalCounterState extends State<CustomVerticalCounter> {
int counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter++;
widget.callback(this.counter);
});
}
void _decrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter--;
widget.callback(this.counter);
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
height: widget.counterHeight,
width: widget.counterWidth,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(widget.borderRadius),
border: Border.all(color: widget.borderColor, width: 1.0),
color: widget.counterColor,
),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
InkWell(
child: Icon(
Icons.add,
size: widget.iconSize,
color: widget.iconColor),
onTap: _incrementCounter,
),
Divider(height: 2,),
Expanded(
child: Container(
// margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 2),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(5),
color: widget.displayColor,
),
child: Column(
children: [
Spacer(),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Visibility(
visible: widget.labelVisible,
child: RotatedBox(
quarterTurns: 3,
child: Text(
widget.counterLabel,
maxLines: 20,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: widget.counterLabelFontSize,
color: widget.counterTextColor
),
),
),
),
Expanded(
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: Text(
'$counter',
maxLines: 1,
overflow: TextOverflow.clip,
softWrap: false,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: widget.counterTextFontSize,
color: widget.counterTextColor
),
),
),
),
],
),
Spacer(),
],
),
),
),
Divider(height: 2,),
InkWell(
child: Icon(
Icons.remove,
size: widget.iconSize,
color: widget.iconColor),
onTap: _decrementCounter,
),
],
),
);
}
}The above code defines a vertical counter widget, which has a column of widgets containing an icon button for incrementing the counter, the display area for the counter value and an icon button for decrementing the counter.
To convert the previous code to the new code, the following changes were made:
- The parent widget was changed from
RowtoColumn. - The order of the widgets was changed so that the increment button was placed at the top of the column and the decrement button was placed at the bottom.
- The
IconButtonwidget was replaced with anInkWellwidget to allow for more flexible styling. - The
VerticalDividerwidget was removed since it is no longer needed in the vertical layout. - The
Expandedwidget was used to ensure that the display area takes up as much space as possible within the column. - The
marginproperty was removed from the display area container since it is no longer needed in the vertical layout.
Apart from these changes, the code remained mostly the same, including the CustomVerticalCounter and _CustomVerticalCounterState class names and their properties.
The widget can be used the same way as the previous widget:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'custom_counter.dart';
import 'custom_vertical_counter.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage>{
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('flutterassets.com'),
),
body: Container(
alignment: Alignment.topCenter,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child:
Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
CustomVerticalCounter(
counterHeight: 100,
counterWidth: 40,
counterLabel: 'Label',
labelVisible: false,
// counterLabelFontSize: 10,
counterTextFontSize: 30,
counterTextColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
iconSize: 20,
iconColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
displayColor: Colors.green.shade100,
counterColor: Colors.green.shade200,
borderRadius: 10,
borderColor: Colors.blue.shade900,
callback: (counter) {
print('$counter');
},
),
SizedBox(width: 10,),
CustomVerticalCounter(
callback: (counter){},
),
],
),
),
);
}
}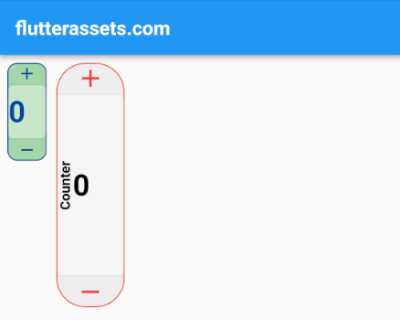
The above code contains a Container with a row of two CustomVerticalCounter widgets.
The first CustomVerticalCounter widget has its properties set, such as the height and width of the counter, the label of the counter, the font size, colours, and border radius. It also has a callback function that will be called every time the counter changes, which in this case, just prints the counter value to the console.
The second CustomVerticalCounter widget is a default widget without any custom properties set. It has a callback function, but it doesn’t do anything in this case.
Overall, the CustomVerticalCounter widget can be used in any Flutter app to display a vertical counter with customizable features, and it can be easily integrated into a page or screen using the Container widget or any other layout widget.




